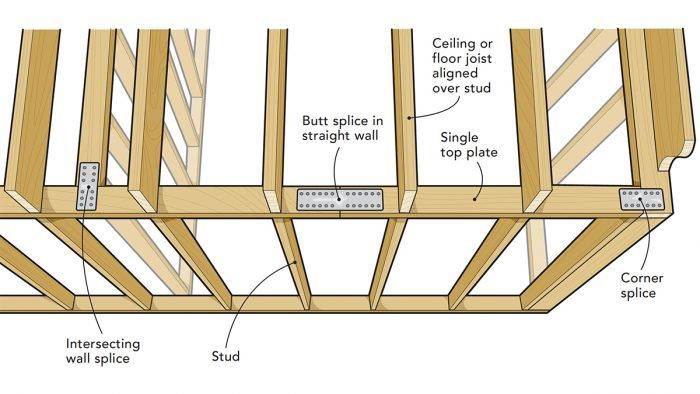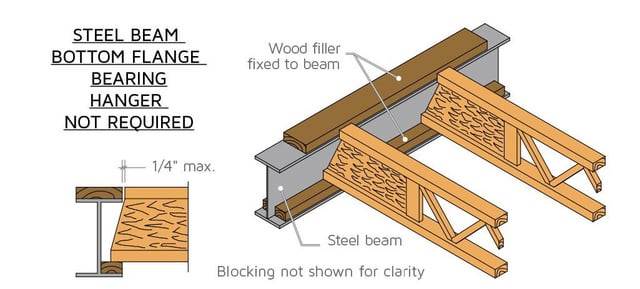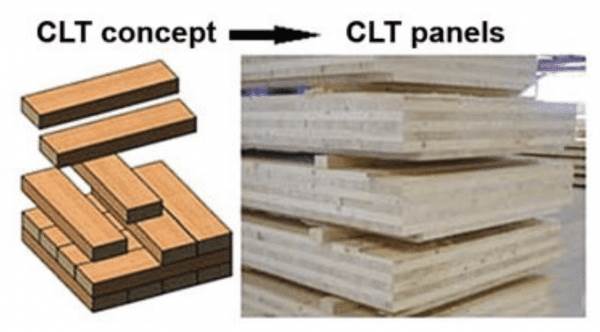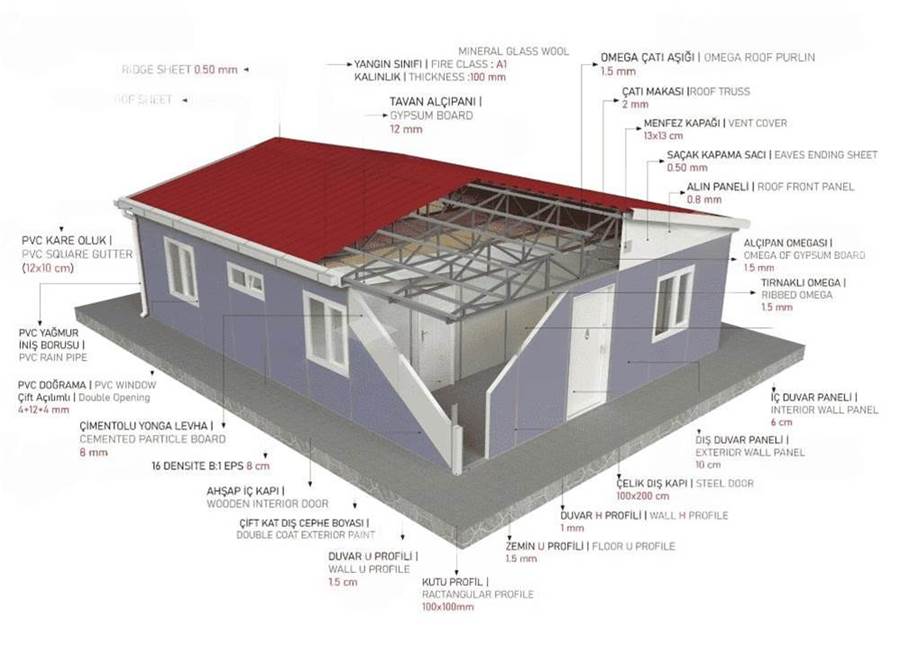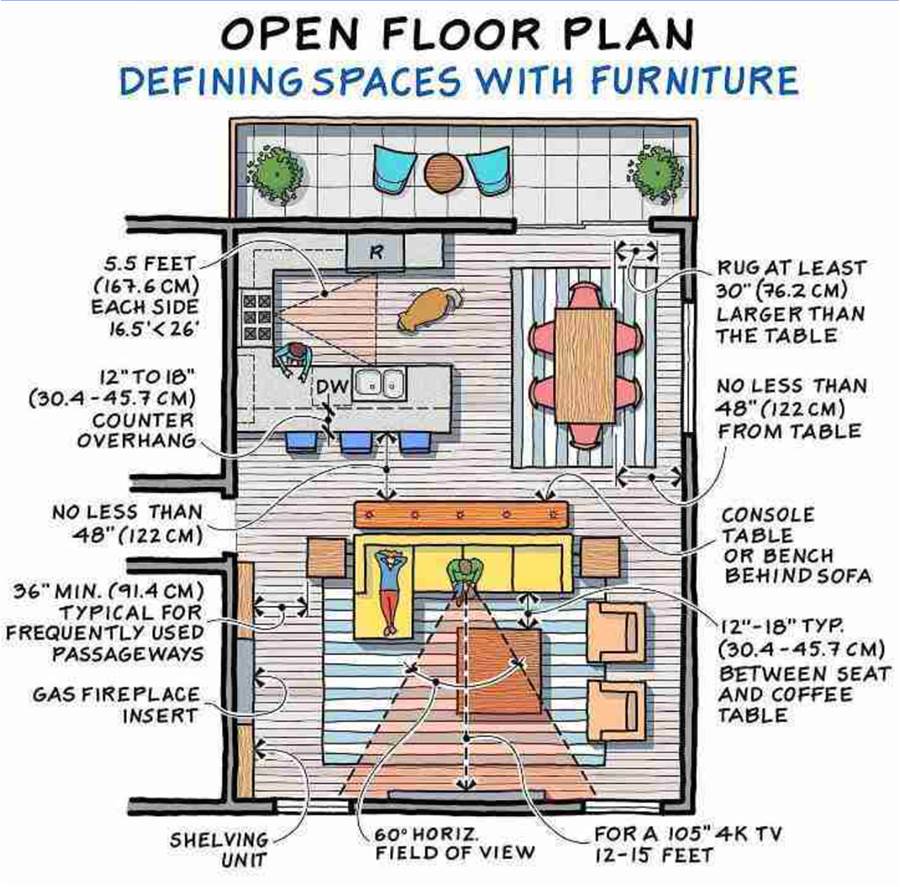
The structural system of a house is more than just its skeleton—it determines how the building stands, how it performs under stress, and how long it lasts. In modern residential construction, different materials and structural methods offer distinct benefits and limitations. This article highlights five common types of house building structures, outlining their characteristics, advantages, and challenges.
Brick–concrete structures, also known as masonry structures, have been used for centuries and remain popular in many regions. Load-bearing walls are built from bricks or blocks, with reinforced concrete floors and roofs.
Advantages:
Affordable and relatively easy to construct with local materials.
Good thermal and acoustic insulation.
Long lifespan when maintained properly.
Limitations:
Limited earthquake resistance compared to modern frame systems.
Less flexible for interior layout changes since walls carry the structural load.
Height restrictions make them unsuitable for tall buildings.
The article is not finished. Click on the next page to continue.
The article is not finished. Click on the next page to continue.
Next page